Figure 2
Download original image
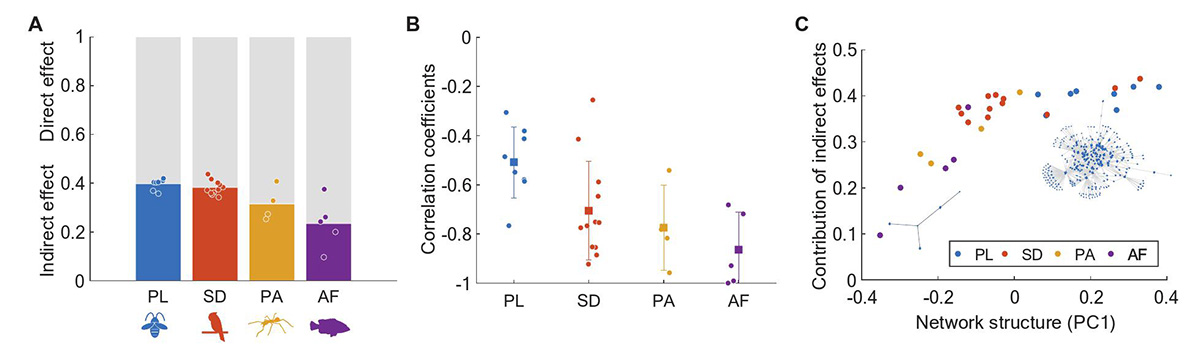
Determinants of indirect effects. (A) Scatters are indirect effects of different types of mutualistic ecosystems; grey bars and colored bars show average direct and indirect effects, respectively. (B) For the majority of all four types of networks, species’ indirect effects have no significant relation to their degrees (especially PL and SD,
![]() ), while in some networks (PA and AF) species’ indirect effects are negatively correlated with their degrees. (C) Indirect effects of multi-types of mutualistic networks increase along the gradient based on PC1 of principal component analysis, where well connected and nested networks (negative PC1 values) have small indirect effects, and modular, heterogeneous, large networks (positive PC1 values) have large indirect effects. The two networks in (C) show different structures (PL/AF) with large/small PC1 values and indirect effects, respectively. In (A)–(C), different colors represent different mutualistic networks: PL: plant-pollinator, SD: seed-dispersal, PA: plant-ant, AF: anemone-fish. Parameters:
), while in some networks (PA and AF) species’ indirect effects are negatively correlated with their degrees. (C) Indirect effects of multi-types of mutualistic networks increase along the gradient based on PC1 of principal component analysis, where well connected and nested networks (negative PC1 values) have small indirect effects, and modular, heterogeneous, large networks (positive PC1 values) have large indirect effects. The two networks in (C) show different structures (PL/AF) with large/small PC1 values and indirect effects, respectively. In (A)–(C), different colors represent different mutualistic networks: PL: plant-pollinator, SD: seed-dispersal, PA: plant-ant, AF: anemone-fish. Parameters:
![]() , threshold
, threshold
![]() .
.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

