Figure 2
Download original image
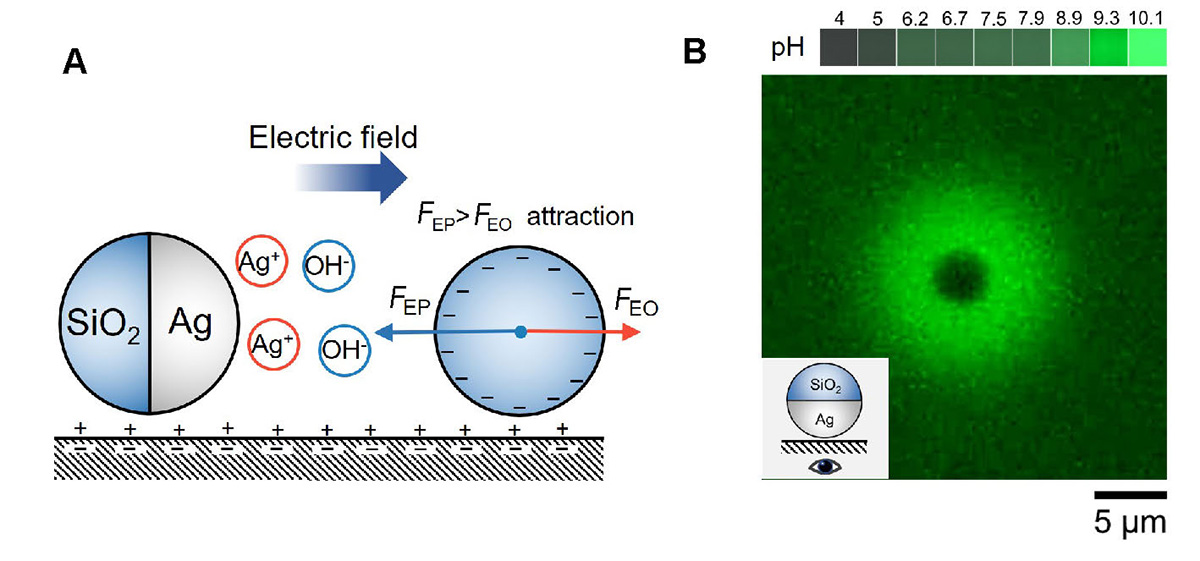
Ag colloids attract each other by ionic diffusiophoresis. (A) Schematic diagram of a SiO2-Ag microsphere attracting an inert microsphere by ionic diffusiophoresis in H2O2. The Ag cap reacts with H2O2 and releases Ag+ and OH−, which leads to a self-generated electric field that points away from the Ag colloid. A negatively charged tracer nearby reacts to this electric field by electrophoretically migrating toward the Ag colloid under the influence of an electrophoretic force FEP. In addition, the electric field causes an electroosmotic flow from the negatively charged bottom substrate that advects the tracer via an electroosmotic draf force FEO. FEP dominates over FEO, so that tracers are attracted to Ag colloids. (B) Fluorescence photograph of SiO2-Ag in 0.01 wt% H2O2. Stronger green fluorescence indicates higher pH values. A pH-sensitive fluorescent dye Solvent Green 7 was used at a concentration of 100 μmol L−1. Blue light of 475 nm and ~75 mW cm−2 was used to excite fluorescence.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

