Figure 4
Download original image
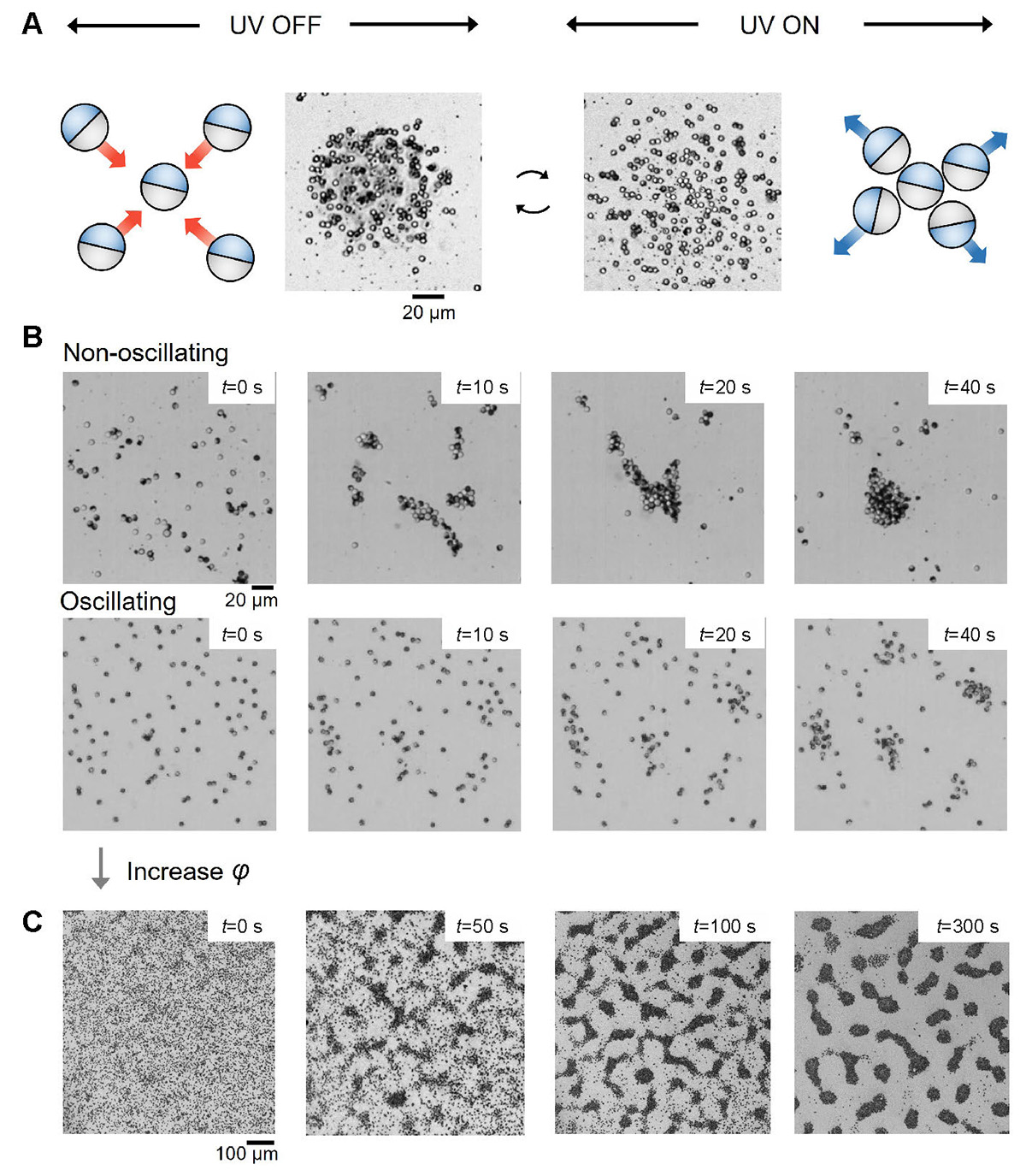
Phase separation of oscillating Ag colloids under intermittent UV illumination. (A) SiO2-Ag colloids repel each other when light is on, but attract each other when light is off. (B) Clustering process of non-oscillating (top) and oscillating (bottom) Ag particles. Top row: photograph of Ag particles (φ = 7.9%) aggregating in 200 μmol L−1 KCl and 0.25 wt% H2O2 aqueous solution. Bottom row: in 200 μmol L−1 KCl and 0.25 wt% H2O2 aqueous solution, Ag particles (φ = 8.1%) aggregated upon switching UV on and off at 0.5 Hz (i.e., 1 s light on+1 s light off = one cycle). Note that Cl− is not necessary for the non-oscillating sample to cluster, but was added only to ensure the same solution composition for both samples. (C) Optical micrographs of the phase separation of oscillating Ag colloids (φ = 17%) at a UV trigger frequency of 0.5 Hz (405 nm, ~126 mW cm−2) at different time instances.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

