Figure 1
Download original image
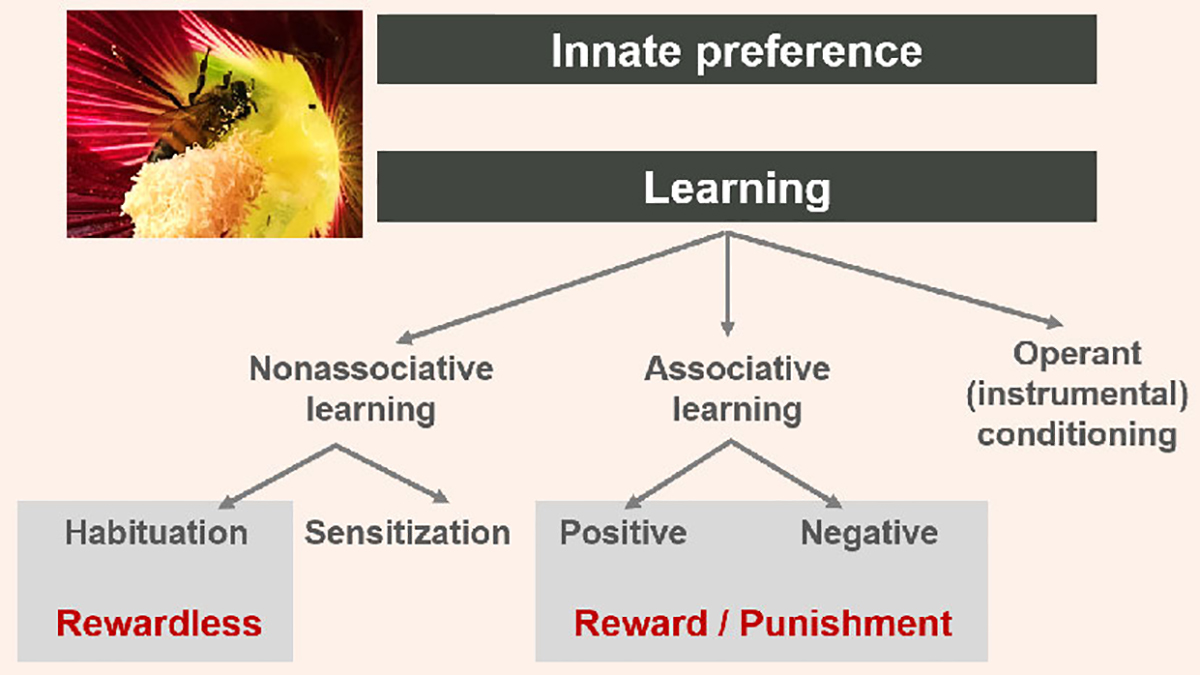
Distinct learning paradigm with their corresponding pollination scenarios. Learning can be broadly categorized into non-associative learning (habituation and sensitization), associative learning and operant (instrumental) conditioning. Associative learning occurs through the pairing of two previously unrelated stimuli, whereas non-associative learning occurs in response to a single stimulus. Associative learning occurs in rewarding or punitive flower visits. Non-associative learning comprises sensitization and habituation, while habituation is more likely to occur in rewardless visiting behavior.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

