Figure 1
Download original image
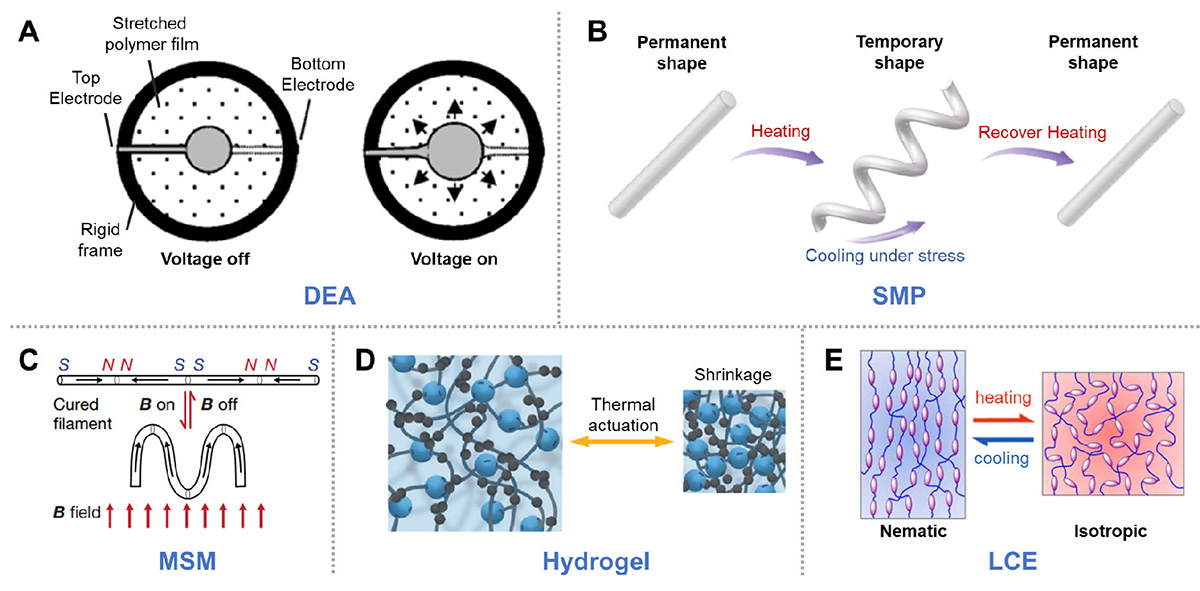
The actuation mechanism of typical soft actuating materials. (A) When subject to high voltage, a strong electrostatic interaction is generated between two electrodes, compressing the film in the thickness direction and expanding it in the area. Reprinted with permission from Ref [6]. (B) After being deformed at a high temperature and fixed into a temporary shape after cooling, shape memory polymer (SMP) can recover to its permanent shape upon heating. Reprinted with permission from Ref [9]. (C) Magnetic soft material (MSM) with programmed magnetic domains exhibits complex shape changes under external magnetic field stimulus. Reprinted with permission from Ref [10]. (D) Thermal stimulated isotropic volumetric change of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) hydrogel. Reprinted with permission from Ref [14]. (E) Upon thermal stimuli, LCE undergoes the nematic-isotropic phase transition, causing a large contraction in the alignment direction. Reprinted with permission from Ref [15].
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

