Figure 6
Download original image
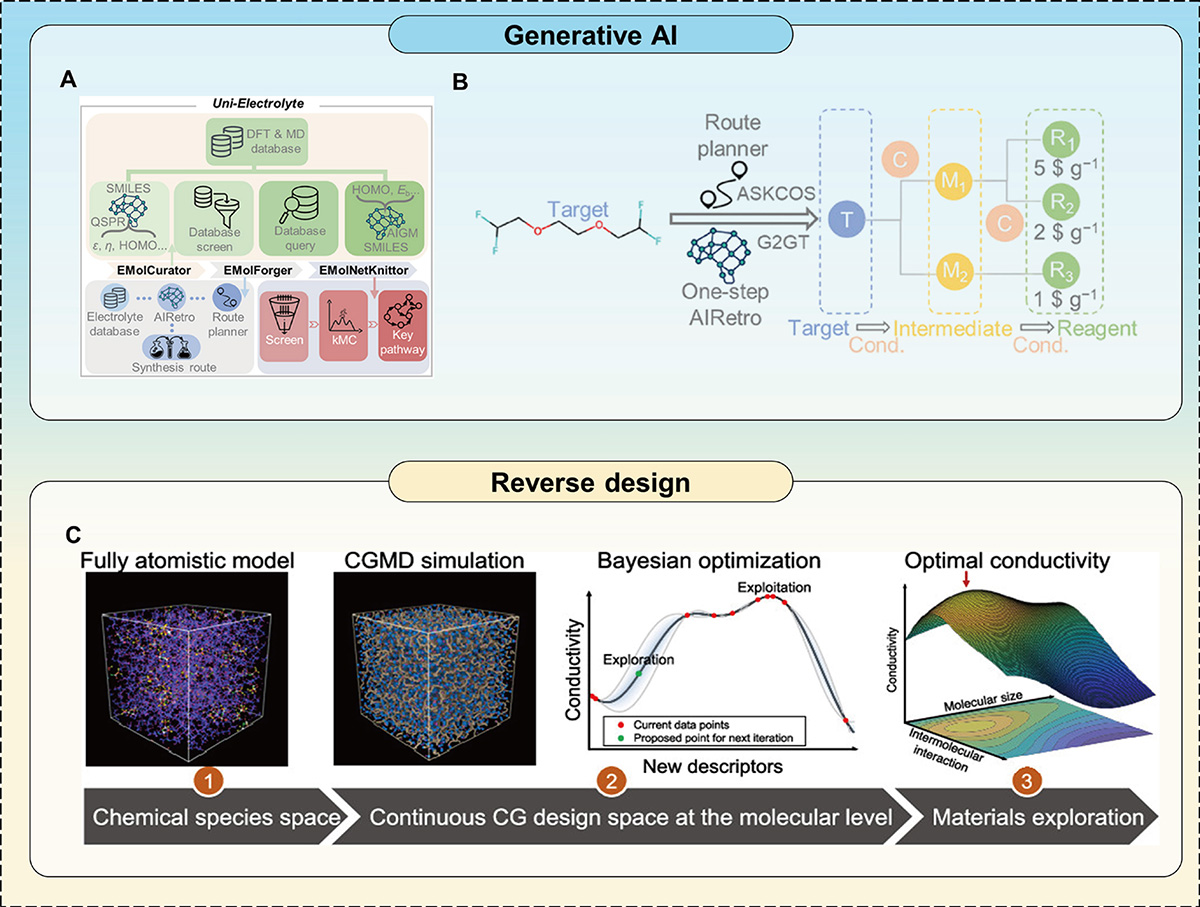
Generative AI and reverse design. This figure illustrates the paradigm of generative and reverse design in BDA, where AI models learn to map target performance to optimal material compositions, molecular structures, or synthesis pathways, thereby accelerating the discovery of next-generation battery components. (A) Schematic representation of the Uni-Electrolyte platform with three modules. The EMolCurator module aims to design new electrolyte molecules. Based on the embedded electrolyte database, QSPR and AI-based generative models were trained. The EMolForger module can predict the synthesis pathways and corresponding reaction conditions of potential electrolyte molecules. It was built with a synthetic route planner and AI-based single-step retrosynthesis predictor. The EMolNetKnittor module assesses the filtered electrolyte species and reaction database to propose chemical reaction networks and perform SEI-product analysis. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [95]. Copyright©2025, Wiley-VCH GmbH. (B) The illustration of the retrosynthesis module. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [95]. Copyright©2025, Wiley-VCH GmbH. (C) Toward designing highly conductive polymer electrolytes by machine learning assisted coarse-grained molecular dynamics. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [96]. Copyright©2020, American Chemical Society.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.

